Protein powders, blends and energy bars are the most sought- after dietary supplements by athletes and fitness enthusiasts. These supplements are valuable in building muscle mass, endurance and tissue repair. The most common type of protein is whey, which is extracted from dairy sources. Moreover, whey protein is extensively studied and is used as a potent supplement in sports nutrition. It is available in two forms, including whey isolate and whey concentrate.

For Enhanced Muscle Mass And Growth Buy From Our Wide Range Of Whey Protein Supplements, Right Here!
What Is Whey Protein?
The protein usually present in protein powders, drinks and bars is obtained from milk. When milk is processed to form cheese or yogurt, the liquid whey is called whey, and it contains quickly digestible proteins, which are referred to as whey protein.
Milk constitutes 20% whey, and the other 80% is made up of the slow-digesting casein proteins. Whey and casein are high-quality milk proteins, as they contain all the essential amino acids needed by the human body. However, whey has a higher edge, and it is beneficial for promoting the production of new protein in the muscles.
Whey proteins are available in several types; however, the most common forms are whey isolate and whey concentrate.
Difference Between Whey Protein Isolate And Whey Concentrate
There are multiple nutritional differences between whey isolate and concentrate; these differences are caused by the way both are processed.
Whey is the liquid collected as a byproduct of cheese or yogurt production; it undergoes several processing steps to improve its protein composition. After the required protein concentration is attained, the liquid can be dried to form whey concentrate powder that comprises up to 80% protein by weight. The remaining 20% of whey concentrate contains carbs and fats.
When processing steps are changed, the fat and carbohydrate content of whey is lowered, after which a whey isolate powder containing 90% and more protein by weight is obtained.
The processing methods used in the production of whey isolate result in higher protein content and lower fat and carbohydrate content per serving. While both have an identical amino acid profile, they are obtained from the same source of proteins.
The table below shows the key nutritional differences between whey isolate and whey concentrate supplements per 100-calorie serving:
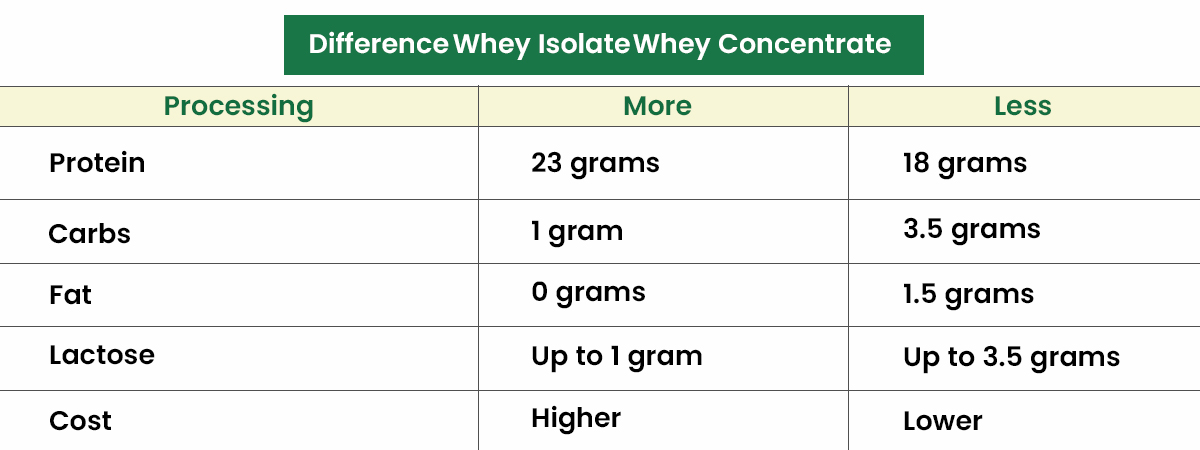
In addition to having lower total carbohydrate content, whey isolate also has lower lactose content. This means that it could be a better choice for those who are lactose intolerant.
Whey isolate has lower lactose content, thus making it an ideal choice for those with lactose intolerance. However, the quantity of lactose content in both whey proteins is likely to be low enough, which is adequate for those with lactose intolerance.
Both Forms Have Similar Benefits
Numerous studies have revealed that whey protein is valuable for healthy and active people. A study has found that whey protein supplements, including whey isolate or concentrate, promote lean muscle mass, endurance and strength.
Though there are minor differences in nutritional value, there is not enough evidence to suggest that whey isolate, and concentrate have different impacts on the human body.
With regards to protein, one of the key factors is your total daily intake. Health experts recommend that the majority of daily protein intake should be met from high-quality sources like dairy, eggs and poultry.
Both whey isolate and concentrate are high-quality proteins, and they offer similar benefits when taken in equivalent doses.
With that in mind, those who are limiting fat, carbohydrate or lactose may choose whey isolate as it is lower than whey concentrates in all these three nutrients. Moreover, these days, many supplements contain a mixture of proteins that includes both whey isolate and whey concentrate.

Also Read: 5 Plant-Based Proteins With More Protein Than Eggs: Nutrition, Health Benefits And Uses
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Whey Concentrate Good for Muscle Gain?
Yes. It effectively stimulates muscle protein synthesis and promotes building muscle mass. For most people, the difference in muscle gain compared to isolate is minimal if total daily protein intake is adequate.
Whey Protein Isolate vs Concentrate Digestion
Whey isolates contain quickly digestible protein, and they are easier on the stomach, especially for those who are lactose intolerant.
Which Is Better for Muscle Building?
Both are effective, but muscle growth depends more on:
Total daily protein intake (1.6–2.2g/kg body weight)
Progressive overload training
Caloric balance
If protein intake is equal, muscle gain differences are negligible.
For Bodybuilding
During the bulking process, protein requirement is higher and calorie need is less, thus whey concentrate is cost-effective.
During cutting down or weight loss, whey isolate is preferable due to fewer calories.
Whey Isolate vs Whey Concentrate for Weight Loss
Whey isolate has slightly fewer calories, zero carbs and high protein density. This makes it slightly better for strict calorie-controlled diets.
However, the difference per scoop is often only 10–20 calories, which is not dramatic.
Whey Isolate vs Whey Concentrate Calories
Caloric per scoop:
Whey Concentrate: ~120 kcal
Whey Isolate: ~105 kcal
The calorie difference is very minimal and not a deciding factor.
Whey Isolate vs Whey Concentrate Protein Content
Concentrate: ~22g protein per scoop
Isolate: ~26g protein per scoop
If you need the most protein per scoop, isolate has the edge.
Can I Take Whey Isolate or Concentrate as a Beginner?
For beginners, whey concentrate would be an ideal and more affordable option. And it supports muscle gain and growth more effectively.
Go for isolate only if you are in a strict calorie deficit state, lactose intolerant and have digestive discomfort.
Whey Protein Side Effects
Whey isolate is generally safe and well-tolerated by most healthy adults.
Possible side effects include:
In rare cases, digestive discomfort.
Skin changes, such as acne issues, occur in a few people.
People with pre-existing kidney disease should avoid it.
Overconsumption may cause GI issues.
Healthy individuals can safely consume whey protein daily within recommended protein ranges.
Which Is Better?
Whey protein comprises numerous fast-digesting proteins and is a common component in most dietary supplements. Two of the most common forms are whey isolate and whey concentrate.
Whey isolate uses different processing methods than whey concentrate, resulting in a higher-protein, lower-carb, lower-fat per-serving option. Whey isolate is an ideal choice for those who are cautious about restricting their fat, carb or lactose intake, and it is typically more expensive. On the other hand, taking a slightly higher amount of whey concentrate can help you get the same quantity of protein as you would get from whey isolate, at a lower cost.
Regardless of which type of protein you choose, whey is a high-quality protein supplement that can help you meet your daily protein needs and fitness goals.
References:
Comparative Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Concentrated, Hydrolyzed, and Isolated Whey Protein Supplementation on Body Composition of Physical Activity Practitioners
Luis Henrique A Castro 1,*, Flávio Henrique S de Araújo 1,
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6769754/
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339775439_Whey_protein_isolate_or_concentrate_combined_with_concurrent_training_does_not_augment_performance_cardiorespiratory_fitness_or_strength_adaptations



 Previous
Previous