Netmeds First Membership
Quick Links
Introduction About GEMER 1 TABLET
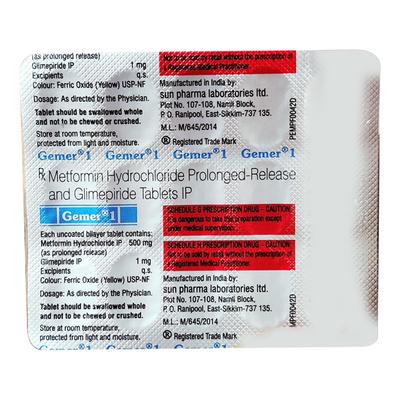
Gemer 1 Tablet contains a combination of two medications such as Glimepiride and Metformin. This combination is used to manage type 2 diabetes and help control blood sugar levels when diet and exercise alone are not enough.
Gemer 1 tablet should be taken with food. To achieve the best results, take it consistently at the same time each day. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage for you, which may be adjusted periodically based on your blood sugar levels and how the medication is working.
Continue taking this medication even if you feel fine or your blood sugar levels are under control. Stopping it without your doctor's guidance could lead to an increase in blood sugar levels, putting you at risk of kidney damage, blindness, nerve issues, and limb loss. Keep in mind that this medication is just one part of a management plan, which should also include a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management as recommended by your doctor. Your lifestyle plays a crucial role in managing diabetes.
Common side effect of this medication includes nausea, stomach upset, dizziness, diarrhea, low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) symptoms such as sweating, dizziness, headache, and shaking, taste changes and upper respiratory tract infection. To avoid this, it is essential to have regular meals and always keep a quick source of glucose, like sugary snacks or fruit juice, on hand. Alcohol can also raise the risk of low blood sugar and should be avoided. Additionally, some individuals may experience weight gain while using this medication.
This medication should not be taken if you have type 1 diabetes mellitus, diabetic ketoacidosis (high blood acid levels), or severe kidney or liver disease. Before using this medication, inform your doctor if you have a history of heart disease, as it may not be appropriate for you. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult with their doctor before taking it. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is recommended, and your doctor may also suggest blood tests to check your blood cell counts and liver function.
Uses Of GEMER 1 TABLET
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Benefits of GEMER 1 TABLET
- Effective blood sugar control: The combination of Glimepiride and Metformin helps regulate blood glucose levels effectively.
- Helps prevent complications: By managing blood sugar, GEMER helps reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
- Convenience: A single tablet with two active ingredients for easy management of diabetes.
- Improves insulin sensitivity: Metformin helps the body use insulin more effectively.
How GEMER 1 TABLET Works
Gemer 1 Tablet which contains a combination of Glimepiride and Metformin, works by controlling blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Glimepiride, a sulfonylurea, stimulates the pancreas to release more insulin, helping to lower blood sugar levels. Metformin, a biguanide, works by reducing the amount of sugar produced by the liver and improving the body's sensitivity to insulin, allowing the cells to use insulin more effectively. Together, these actions help to control high blood sugar, improving overall glucose regulation in individuals with diabetes.
How to use GEMER 1 TABLET
Follow your doctor's instructions regarding the exact dosage. Do not exceed the recommended daily dosage.
How to Take Gemer 1 tablet?
- Take one tablet daily with meal to reduce the chance of stomach upset.
- Swallow the tablet whole with a glass of water. Do not crush or chew the medication.
- For best results, take the tablet at the same time each day.
What if I forgot to take GEMER 1 TABLET
- If you forget to take your dose, take it as soon as you remember.
- Do not take two doses to make up for a missed dose. This could increase your risk of side effects.
- If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and take your regular dose at the usual time.
Side Effects Of GEMER 1 TABLET
Like all medicines, Gemer 1 tablet may cause certain side effects in some individuals, although not everybody gets them.
The most common side effects of taking Gemer 1 tablet are:
- Nausea
- Stomach upset
- Dizziness
- Diarrhea
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
- Taste changes
- Upper respiratory tract infection
When to consult your doctor?
- Severe Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar) symptoms such as sweating, shaking, dizziness, confusion, irritability, rapid heartbeat, blurred vision, and loss of consciousness.
- Lactic Acidosis symptoms such as unusual muscle pain, difficulty breathing, dizziness, feeling cold, tiredness, or lightheadedness.
- Allergic Reactions symptoms such as rash, itching, swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, or trouble breathing.
- Gastrointestinal Problems symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Heart-related Symptoms such as chest pain, unusual fatigue, or shortness of breath
- Liver Problems symptoms such as yellowing of the skin or eyes, dark urine, or abdominal pain.
- Kidney Problems symptoms such as decreased urine output, swelling in the ankles or feet, unusual fatigue
How To Manage Side Effects
Diarrhea
- Drink Fluids: Drink clear fluids such as water, broths, and oral rehydration solutions (ORS).
- Electrolytes: If you are losing a lot of fluids (for example, from frequent diarrhea), consider drinking an electrolyte solution to help replenish lost minerals like potassium and sodium.
- BRAT Diet: Try to take Bananas, Rice (white rice), Apple sauce and Toast (plain, without butter) to control diarrhoea management.
- Avoid Certain Foods: While recovering avoid the following food items such as fatty, greasy, or fried foods, spicy foods, dairy products (especially if you have a temporary lactose intolerance), caffeinated drinks and alcohol and artificial sweeteners like sorbitol.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: You can take over-the-counter anti-diarrheal medications such as loperamide, Bismuth subsalicylate if appropriate for you. Follow the recommended dosage.
Dizziness Or Drowsiness
- Sit or Lie Down: If you feel dizzy, sit down or lie down immediately to prevent falling. Keep your head still and close your eyes if needed.
- Hydrate: Dehydration can cause dizziness, so drink water or electrolyte-replenishing drinks like sports drinks.
- Avoid Sudden Movements: When standing or sitting, do so slowly to avoid triggering dizziness. Take your time when getting up.
- Eat Small, Regular Meals: Low blood sugar can cause dizziness, so eat small meals throughout the day and avoid skipping meals.
- Fresh Air: Sometimes dizziness can be alleviated by taking slow, deep breaths in a well-ventilated area.
Nausea And Vomiting
- Eat Small, Frequent Meals: Avoid heavy or greasy foods. Opt for bland foods like crackers, toast, or bananas.
- Stay Hydrated: Sip on clear fluids like water, ginger tea, or electrolyte drinks, Avoid caffeinated and carbonated beverages.
- Ginger: Ginger is a natural remedy for nausea. Try ginger tea, ginger candies, or ginger ale (ensure it contains real ginger).
- Avoid Strong Odors: Minimize exposure to smells that might trigger nausea, such as perfumes or cooking odors.
Warning & Precautions
Pregnancy
ContraindicatedGemer 1 tablet is not recommended for use during pregnancy. Although there are limited studies in humans, animal studies have shown harmful effects on the developing baby. It is important to consult your doctor before taking this medication.
Breastfeeding
ContraindicatedGemer 1 tablet is not recommended for use during breastfeeding. Data suggests that the drug may cause toxicity to the baby. It is important to consult your doctor before taking this medication.
Driving and Using Machines
Use with CautionDo not drive or operate machines if you experience signs of high/low blood sugar or visual problems.
Alcohol
Consult your doctorAlcohol can raise the risk of lactic acidosis and hypoglycemia, so it is recommended to limit or avoid alcohol consumption while using Gemer 1 tablet.
Kidney
Consult your doctorGemer 1 tablet is not recommended for use in patients with severe kidney disease and should be used with caution in patients with kidney disease and your dose will be adjusted if needed depending upon kidney function. Please consult your doctor before taking it.
Liver
Consult your doctorGemer 1 tablet is not recommended if you have severe liver disease and should be used with caution in patients with liver disease and your dose will be adjusted if needed depending upon liver function. Please consult your doctor before taking it.
Allergy
ContraindicatedDo not take this medication if you are allergic to Glimepiride or Metformin or other sulfonylureas (such as glipizide, glibenclamide) or sulfonamides (such as sulfamethoxazole).
Heart Disease
ContraindicatedGemer 1 tablet is not recommended for use in patients with acute heart problems or recently had a heart attack or have severe circulatory problems or breathing difficulties (signs of heart failure). Please consult your doctor before taking it.
Use In Pediatrics
ContraindicatedGemer 1 tablet is not recommended for use in children and adolescents (under 18 years of age). Consult your pediatrician before giving it.
Use In Geriatrics
Consult your doctorGemer 1 tablet is not recommended for use in elderly patients (aged 75 years or above) and should be used with caution in elderly patients (aged 65 years or above), especially in patients with impaired kidney function. Your doctor may assess your kidney function more frequently during management with this medicine.
Other Warnings for GEMER 1 TABLET
Before taking Gemer 1 tablet inform your doctor if you:
- are recovering from injury, operation, infections with fever, or from other forms of stress
- have glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency
- have various factors which could increase the risk of low blood sugar levels (such as undernourishment, irregular mealtime, missed or delayed meal or period of fasting, change in diet, hormone-induced disorders)
Who should not take [GBNKEYWORD
Gemer 1 tablet is not recommended for use, if you have:
- type 1 diabetes mellitus
- diabetic ketoacidosis
- uncontrolled diabetes or ketoacidosis
- dehydration
- severe infection
Safety Advice
- Follow your doctor's instructions regarding the exact dosage.
- Do not exceed the recommended daily dosage.
- Take one tablet daily with meal to reduce the chance of stomach upset.
- Swallow the tablet whole with a glass of water. Do not crush or chew the medication.
- For best results, take the tablet at the same time each day.
- Follow the prescribed diet and exercise plan along with taking this medication for best results.
- Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly while taking this medicine.
- Alcohol can raise the risk of lactic acidosis and hypoglycemia, so it is recommended to limit or avoid alcohol consumption while using Gemer 1 tablet.
- Let your doctor know if you have kidney problems or liver problems.
- Let your doctor know If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant or breastfeeding women.
- Do not suddenly stop taking the medication without consulting your doctor, as this can lead to uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
- Store Gemer 1 tablet at room temperature, away from moisture and heat, in a dry place, and out of reach of children.
- Make sure to keep regular follow-up appointments with your doctor to track your progress and adjust your medication as needed.
Diet and Lifestyle Advice
What are some diabetes-friendly foods that complement the effectiveness of GEMER 1 Tablet 15 in controlling blood sugar, such as low-carb and high-fiber options?
|
Food Item |
Type |
Nutritional Benefit |
Explanation |
|
Leafy Greens (Spinach, Kale, etc.) |
Vegetables |
Low in carbs, high in fiber and antioxidants |
Helps regulate blood sugar and provides essential nutrients without spiking glucose. |
|
Broccoli |
Vegetables |
High in fiber, low in carbs, rich in vitamins and minerals |
Aids in blood sugar regulation and provides a feeling of fullness. |
|
Cauliflower |
Vegetables |
Low in carbs, high in fiber and vitamin C |
Supports weight management and helps manage blood sugar levels effectively. |
|
Zucchini |
Vegetables |
Low in carbs, high in fiber |
A great low-calorie, high-fiber vegetable that doesn’t spike blood sugar. |
|
Chia Seeds |
Seeds |
High in fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, low in carbs |
Supports digestion, reduces inflammation, and helps stabilize blood sugar. |
|
Flaxseeds |
Seeds |
High in fiber, low in carbs, rich in healthy fats |
Helps regulate blood sugar and improve heart health. |
|
Berries (Strawberries, Blueberries, etc.) |
Fruits |
High in fiber, low glycemic index |
Provides antioxidants and has a minimal impact on blood sugar when consumed in moderation. |
|
Avocados |
Fruits |
High in healthy fats, low in carbs, high in fiber |
Promotes satiety, lowers blood sugar spikes, and supports heart health. |
|
Eggs |
Protein |
Low in carbs, high in protein, vitamins, and minerals |
Provides a steady energy source and doesn’t cause a spike in blood sugar. |
|
Greek Yogurt (unsweetened) |
Dairy |
High in protein, low in carbs |
Contains probiotics that can aid digestion and support healthy blood sugar levels. |
|
Lentils |
Legumes |
High in fiber and protein, moderate carbs |
A good source of plant-based protein that helps stabilize blood sugar. |
|
Chickpeas |
Legumes |
High in fiber and protein, moderate carbs |
Lowers the glycemic load and supports stable blood sugar levels. |
|
Almonds |
Nuts |
High in fiber, low in carbs, rich in healthy fats |
Helps improve insulin sensitivity and maintains stable blood sugar. |
|
Coconut Oil |
Fats |
Low in carbs, contains medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) |
Supports fat metabolism and has a minimal effect on blood sugar. |
|
Shirataki Noodles |
Low-carb substitute |
Extremely low in carbs, high in fiber |
A great pasta alternative for blood sugar control due to its low glycemic index. |
These foods are chosen for their ability to help control blood sugar, manage insulin sensitivity, and provide a steady source of energy without causing spikes in blood glucose levels. Pairing these foods with medications like GEMER 1 can help achieve better glycemic control. Always consult your doctor or nutritionist before making any significant dietary changes, especially if you are on medication for diabetes.
What are the benefits of regular physical activity in managing diabetes, and how does it work alongside GEMER 1 Tablet 15's?
|
Aspect |
Importance of Regular Physical Activity |
Role of GEMER 1 Tablet 15 |
Combined Effect |
|
Blood Sugar Control |
Regular exercise helps to lower blood sugar levels by improving insulin sensitivity. |
GEMER 1 Tablet 15 contains a combination of drugs that help lower blood sugar. |
Together, they improve blood sugar regulation effectively. |
|
Weight Management |
Physical activity helps in weight loss or maintenance, reducing risk factors. |
GEMER 1 Tablet 15 aids in glucose control, supporting weight management efforts. |
Together, they enhance weight control, reducing risk of complications. |
|
Cardiovascular Health |
Exercise strengthens the heart and improves circulation, reducing cardiovascular risk. |
GEMER 1 Tablet 15 can help with lowering blood sugar and may reduce risks of heart disease. |
Combined, they help maintain a healthy heart and reduce diabetes-related complications. |
|
Improved Insulin Sensitivity |
Exercise enhances the body's ability to use insulin efficiently, reducing insulin resistance. |
GEMER 1 Tablet 15 supports insulin function, making glucose utilization more effective. |
The combination works to increase insulin sensitivity and support glucose metabolism. |
|
Energy Levels |
Regular physical activity boosts overall energy and reduces fatigue. |
GEMER 1 Tablet 15 can reduce symptoms of fatigue caused by high blood sugar levels. |
Together, they help sustain better energy levels throughout the day. |
|
Mental Health Benefits |
Physical activity reduces stress, anxiety, and depression, improving overall mood. |
GEMER 1 Tablet 15 may help stabilize mood by managing blood sugar fluctuations. |
Combined, they contribute to better mental health and overall well-being. |
Drug - Drug interaction
Inform your physician if you are taking any of the following medicine before taking Gemer 1 tablet:
1. Insulin and Other Oral Hypoglycemics
- Interaction: Combining Gemer 1 tablet with insulin or other oral hypoglycemics (such as sulfonylureas) may increase the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) due to enhanced insulin secretion and glucose uptake.
- Effect: The risk of severe hypoglycemia is increased, leading to symptoms like dizziness, sweating, confusion, shakiness, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness or coma.
- Management: To manage the risk of hypoglycemia, close monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential. Adjustments to the doses of insulin or other oral hypoglycemics should be considered, especially during physical activity or fasting. Patients should be educated on recognizing early signs of hypoglycemia and how to treat it (e.g., consuming quick-acting carbohydrates).
2. Cholesterol-lowering Drugs (Statins)
- Interaction: Gemer 1 tablet may interact with statins (e.g., atorvastatin, simvastatin) used to lower cholesterol. Although the interaction is not direct, both drugs can affect glucose metabolism. Statins may increase blood sugar levels, while Glimepiride and Metformin work to lower them.
- Effect: The use of statins along with Gemer could lead to a destabilization in blood sugar control. Some patients may experience an increase in blood glucose levels while on statins.
- Management: Regular monitoring of both cholesterol levels and blood glucose is critical. If blood sugar control worsens, dosage adjustments of either Gemer or the statin may be required. Patients should be informed about the potential impact on blood glucose and encouraged to monitor their levels more frequently. A lifestyle approach (diet, exercise) may also help manage both cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
3. Anticoagulants (e.g., Warfarin)
- Interaction: Both Metformin and Glimepiride can interact with anticoagulants like warfarin, affecting their efficacy. Metformin may alter kidney function, impacting warfarin metabolism, while Glimepiride could enhance the effects of warfarin by interacting with protein-binding sites.
- Effect: The interaction may increase the risk of bleeding due to enhanced anticoagulant effects. Patients may experience bruising, prolonged bleeding times, or even spontaneous bleeding.
- Management: Regular monitoring of INR (International Normalized Ratio) levels is essential for patients on both anticoagulants and Gemer. Close monitoring helps ensure that warfarin doses are appropriately adjusted to prevent bleeding complications. Patients should be advised to report any unusual bleeding or bruising immediately.
4. Beta-blockers (e.g., Atenolol, Metoprolol)
- Interaction: Beta-blockers, commonly used for heart conditions, can mask the symptoms of hypoglycemia (such as tremors and palpitations) caused by Glimepiride.
- Effect: Beta-blockers may reduce the body's ability to recognize hypoglycemia symptoms, leading to delayed treatment and potentially more severe hypoglycemia.
- Management: Patients on both medications should be advised to monitor their blood glucose levels regularly. Healthcare providers may consider adjusting the beta-blocker dose or switching to a different class of medications if hypoglycemia symptoms become unmanageable.
5. Corticosteroids (e.g., Prednisone)
- Interaction: Corticosteroids can raise blood glucose levels by increasing gluconeogenesis (the production of glucose by the liver). This can interfere with the blood sugar-lowering effect of Gemer.
- Effect: The combination may lead to hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), requiring closer monitoring and possible dose adjustment of Gemer.
- Management: Blood glucose levels should be monitored more frequently, especially during corticosteroid therapy. The Gemer dose may need to be adjusted, and patients should be educated on recognizing signs of hyperglycemia (e.g., increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue).
6. Diuretics (e.g., Furosemide, Hydrochlorothiazide)
- Interaction: Diuretics, particularly thiazide diuretics, can reduce the effectiveness of Metformin by increasing blood glucose levels. Additionally, diuretics can lead to electrolyte imbalances, which may worsen the effects of Glimepiride.
- Effect: The combination of Gemer and diuretics can cause increased blood sugar levels, dehydration, or electrolyte imbalances (such as low potassium), which may increase the risk of cardiovascular issues.
- Management: Careful monitoring of electrolytes (especially potassium), blood glucose levels, and hydration status is recommended. Adjustments to Gemer dosages may be needed, and patients should be advised to report any signs of dehydration or electrolyte disturbances.
7. Alcohol
- Interaction: Alcohol can interact with Gemer and increase the risk of both hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis (a rare but serious side effect of Metformin).
- Effect: Alcohol consumption can lower blood sugar levels, particularly in combination with Glimepiride, and may lead to severe hypoglycemia. It can also impair the liver’s ability to clear Metformin, increasing the risk of lactic acidosis.
- Management: Patients should be advised to limit alcohol consumption or avoid it entirely, especially in large amounts. They should also be educated about the symptoms of hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis (e.g., dizziness, fatigue, nausea, breathing difficulties) and seek medical help if these occur.
Synopsis
| Drug | : | Glimepiride, Metformin |
| Pharmacological Category | : | Sulfonylureas, Biguanides |
| Therapeutic Indication | : | Type II diabetes mellitus |
| Dosage Forms | : | Tablet |
More Information
Why Choose GEMER 1 Tablet for Managing Diabetes?
- Combination Therapy: Gemer 1 typically combines two active ingredients Glimepiride (a sulfonylurea) and Metformin (a biguanide). This combination helps control blood sugar through different mechanisms, providing better overall control compared to using either drug alone.
- Glimepiride: As a sulfonylurea, it stimulates the pancreas to produce more insulin, which is helpful for lowering blood sugar, especially after meals.
- Metformin: This drug works by reducing the liver's production of glucose and improving the body’s sensitivity to insulin. It helps keep blood sugar levels stable, particularly during fasting periods.
- Dual Action: The combination of these two medications works synergistically to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce glucose production, and enhance glucose uptake by cells, making it easier for people with type 2 diabetes to manage their condition.
- Convenience: Gemer 1 is typically taken once a day, making it easier for patients to stick to their medication regimen compared to medications that require multiple daily doses.
- Proven Efficacy: The combination of glimepiride and metformin has been extensively studied and shown to be effective in lowering HbA1c (a marker of long-term blood sugar control) in patients with type 2 diabetes.
- Improved Quality of Life: By better controlling blood sugar levels, Gemer 1 can help reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, leading to a better quality of life for patients.
In what situations might Gemer 1 Tablet 15's be a better choice compared to other medications, and how can users decide when it is more appropriate to use?
1. Patients with Poor Blood Sugar Control on Diet and Exercise Alone:
- Indication: GEMER 1 is often prescribed when lifestyle changes (diet and exercise) alone are not enough to control blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- Why Choose GEMER 1: This combination works in two ways: Glimepiride helps the body produce more insulin, while Metformin improves insulin sensitivity and reduces glucose production by the liver. This can be more effective than using Metformin or a sulfonylurea (like Glimepiride) alone.
2. Patients with Insulin Resistance and Insulin Deficiency:
- Indication: Type 2 diabetes is often characterized by both insulin resistance (where the body doesn’t respond well to insulin) and a gradual decline in insulin production.
- Why Choose GEMER 1: Metformin addresses insulin resistance, and Glimepiride helps with insulin secretion. For patients showing characteristics of both problems, this combination can address both aspects of the disease more effectively than a single-drug treatment.
3. Those Who Cannot Tolerate Other Medications:
- Indication: Some patients experience side effects with other diabetes medications, such as sulfonylureas alone or certain GLP-1 agonists.
- Why Choose GEMER 1: GEMER 1 combines Glimepiride with Metformin, which has a different side effect profile than other medications, especially insulin or other sulfonylureas, and can be better tolerated by some people.
4. Patients Who Need Blood Sugar Control without the Risk of Weight Gain:
- Indication: Some diabetes medications, like insulin or certain sulfonylureas, can lead to weight gain.
- Why Choose GEMER 1: Metformin is known for having a neutral or even weight-reducing effect, making GEMER 1 a good option for people who need blood sugar control but want to avoid weight gain.
5. Those with a Risk of Cardiovascular Disease:
- Indication: Patients with type 2 diabetes often have a higher risk of cardiovascular complications.
- Why Choose GEMER 1: Metformin has been shown to have beneficial effects on heart health and is often the first-line treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes who are at risk for cardiovascular disease. Combining it with Glimepiride can be more effective in certain patients than using other combinations, especially when other diabetes medications like thiazolidinediones or insulin are less suitable.
6. Patients with a Higher Risk of Hypoglycemia from Other Medications:
- Indication: Some diabetes drugs, particularly insulin and sulfonylureas, can cause hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
- Why Choose GEMER 1: While Glimepiride can cause hypoglycemia, when combined with Metformin, the risk may be reduced compared to using higher doses of Glimepiride alone. Additionally, Metformin works by reducing glucose production in the liver, which has a more gradual effect, lowering the chances of sudden drops in blood sugar.
7. Patients Who Need Both an Oral Agent and Insulin Secretion Support:
- Indication: If a patient is struggling with both high blood sugar levels and a decreased ability to secrete insulin, a combination medication might be necessary.
- Why Choose GEMER 1: This medication can help the pancreas release more insulin through Glimepiride, while also addressing insulin resistance and liver glucose production via Metformin. For patients needing a dual-action approach, GEMER 1 can be more beneficial than a single agent like insulin or just Metformin.
How can individuals with type 2 diabetes who are overweight or obese safely lose weight while managing their condition, particularly in relation to medications like Metformin and Glimepiride?
Weight loss is a significant goal for many people with type 2 diabetes, as it can help improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and reduce the risk of complications. If you are using medications like Metformin and Glimepiride, it is important to approach weight loss safely and in a way that complements your management. Here, how these medications interact with weight loss and some tips for managing both diabetes and weight:
1. Metformin and Weight Loss
Metformin is often prescribed as a first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes. While its primary role is to help lower blood sugar by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing glucose production in the liver, it can have a mild effect on weight loss for some people. This is generally due to:
- Appetite suppression: Some people may experience a reduced appetite while on Metformin, which could lead to eating fewer calories.
- Improved insulin sensitivity: Better insulin sensitivity can reduce insulin resistance, which is associated with weight gain and difficulty losing weight.
- Modest weight loss: Over time, people on Metformin may experience a slight reduction in weight, but this is usually small and gradual (often around 5-10% of body weight).
2. Glimepiride and Weight Loss
Glimepiride is a sulfonylurea medication that helps stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin. While effective at controlling blood sugar, it can sometimes cause weight gain. This is because:
- Increased insulin levels: Higher insulin levels can lead to fat storage in the body, which might result in weight gain if not carefully managed.
- Risk of hypoglycemia: Glimepiride increases insulin secretion, which can sometimes cause low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). If blood sugar drops too low, people may eat more to bring it back up, which can inadvertently lead to weight gain.
Because of the potential for weight gain, it’s important to be mindful of your eating habits and monitor your blood sugar levels carefully while on Glimepiride.
3. Safe Weight Loss Strategies for People with Type 2 Diabetes
When working to lose weight with diabetes, focusing on a balanced, sustainable approach is key. Here are some tips:
- Eat a balanced, nutrient-rich diet: Focus on whole foods like vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. A lower-carb diet may help manage blood sugar levels more effectively, but it’s important to work with a healthcare professional to determine the best diet for your individual needs.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, promotes weight loss, and supports overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise (e.g., brisk walking) each week, including both aerobic and strength-training activities.
- Monitor blood sugar levels: Regular monitoring is crucial, especially when trying new diets or exercise routines. This will help you understand how certain foods and activities affect your blood sugar.
- Consider smaller, more frequent meals: Eating smaller meals more frequently throughout the day may help with hunger control and blood sugar management.
- Hydrate well: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and support your body's functions. Sometimes thirst can be mistaken for hunger, which could lead to overeating.
4. Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Before starting any weight loss plan, it is important to talk with your healthcare provider. They can help guide you on the best approach, taking into account your medications, diabetes management plan, and overall health.
In some cases, they may also refer you to a registered dietitian or diabetes educator who can help you develop a personalized plan for weight loss and blood sugar control.
5. Other Considerations
- Medication adjustments: If weight loss becomes difficult due to medication side effects, your healthcare provider may consider adjusting your management plan. There are other medications like GLP-1 agonists (e.g., semaglutide) that may support both blood sugar control and weight loss.
- Mental health and support: Losing weight can be challenging, and managing diabetes on top of that can feel overwhelming. Joining a support group or seeking counseling can help with motivation and coping strategies.
While Metformin may have a slight weight-loss benefit, Glimepiride may make weight management more challenging. A balanced approach to diet, exercise, and careful medication management, alongside support from your healthcare team, can help you safely manage your weight and diabetes.
How does GEMER 1 Tablet 15 compare to other diabetes medications, such as other oral treatments or insulin, in managing type 2 diabetes?
|
Medication |
Active Ingredients |
Mechanism of Action |
Common Dosage |
Benefits |
Side Effects |
Comparison to GEMER 1 |
|
GEMER 1 Tablet |
Glimepiride, Metformin |
- Glimepiride: Increases insulin release from the pancreas. |
1 tablet once or twice a day |
- Dual action: controls blood sugar by increasing insulin & reducing glucose production. |
- Gastrointestinal issues (nausea, diarrhea). |
- Well-rounded option for many with type 2 diabetes. |
|
Metformin (Single Drug) |
Metformin |
- Reduces glucose production in the liver. |
500 mg to 2000 mg daily, depending on the response |
- First-line treatment for type 2 diabetes. |
- Gastrointestinal discomfort (diarrhea, nausea). |
- GEMER includes a sulfonylurea (Glimepiride), which may be beneficial for patients who need additional insulin release. |
|
Sulfonylureas (e.g., Glibenclamide) |
Glibenclamide (or other sulfonylureas) |
- Stimulates insulin release from the pancreas. |
2.5 mg to 20 mg daily |
- Effective at reducing blood sugar. |
- Hypoglycemia (especially in elderly or those with renal impairment). |
- GEMER provides a dual mechanism (Metformin + Glimepiride) to address both insulin sensitivity and insulin release. |
|
DPP-4 Inhibitors (e.g., Sitagliptin) |
Sitagliptin |
- Inhibits the enzyme DPP-4, which increases insulin release and reduces glucagon production. |
100 mg daily |
- Weight-neutral. |
- Upper respiratory infections. |
- GEMER has a broader action on insulin and glucose regulation, while DPP-4 inhibitors mainly impact insulin release and glucagon. |
|
SGLT-2 Inhibitors (e.g., Empagliflozin) |
Empagliflozin |
- Inhibits sodium-glucose co-transporter 2, which leads to increased excretion of glucose through the urine. |
10 mg to 25 mg daily |
- Helps with weight loss. |
- Urinary tract infections. |
- GEMER works by addressing insulin resistance and release, while SGLT-2 inhibitors focus on glucose elimination. |
|
Insulin (e.g., Insulin Glargine) |
Insulin (varies by type) |
- Replaces or supplements insulin in the body to control blood sugar. |
Dosing depends on the individual (e.g., once daily for long-acting) |
- Can achieve tighter glucose control. |
- Weight gain. |
- GEMER may be used as an initial treatment for type 2 diabetes, while insulin is often reserved for more advanced cases or uncontrolled blood sugar. |
FAQs About GEMER 1 TABLET
Q: What is GEMER 1 Tablet 15's used for?
A: GEMER 1 Tablet 15's is a combination medication used to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus. It contains two active ingredients: Glimepiride and Metformin. Glimepiride helps increase insulin production, while Metformin improves the body’s sensitivity to insulin, helping to control blood sugar levels. It is commonly prescribed when diet and exercise alone are insufficient to manage blood sugar.
Q: How does GEMER 1 Tablet 15's work to control blood sugar?
A: GEMER 1 Tablet 15's works by combining two mechanisms. Glimepiride stimulates the pancreas to produce more insulin, helping to lower blood glucose levels. Metformin, on the other hand, works by reducing the amount of glucose produced by the liver and improving the body's response to insulin. Together, these actions help keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Q: Can GEMER 1 Tablet 15's be used for type 1 diabetes?
A: No, GEMER 1 Tablet 15's is not recommended for type 1 diabetes. It is specifically formulated for people with type 2 diabetes, where the body either does not produce enough insulin or is resistant to insulin. Type 1 diabetes requires insulin therapy, and GEMER 1 is not suitable for insulin-dependent patients.
Q: How long does it take for GEMER 1 Tablet 15's to lower blood sugar levels?
A: The time it takes for GEMER 1 Tablet 15's to lower blood sugar levels can vary. Some patients may see improvements within a few days, but it generally takes 1 to 2 weeks to notice significant changes in blood sugar control. It is important to follow your doctor’s guidance and monitor blood sugar levels regularly to assess effectiveness.
Q: Can GEMER 1 Tablet 15's be used with other diabetes medications?
A: Yes, GEMER 1 Tablet 15's can be used in combination with other diabetes medications, depending on your healthcare provider's recommendations. However, it is essential to consult with your doctor before combining it with other medications to avoid possible drug interactions or complications.
Q: What happens if I forget to take GEMER 1 Tablet 15's?
A: If you forget to take GEMER 1 Tablet 15's, take it as soon as you remember, unless it is almost time for your next dose. In that case, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular schedule. Never take two doses to make up for a missed one, as this could lead to a risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
Q: Can I stop taking GEMER 1 Tablet 15's once my blood sugar is under control?
A: You should not stop taking GEMER 1 Tablet 15's without consulting your doctor, even if your blood sugar levels are under control. Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition, and stopping medication could cause blood sugar levels to rise again. Your doctor may adjust your treatment plan based on your progress.
Q: Is GEMER 1 Tablet 15's safe for long-term use?
A: Yes, GEMER 1 Tablet 15's is generally considered safe for long-term use when taken as prescribed. However, it is important to have regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor for any potential side effects, such as changes in kidney or liver function, and to ensure ongoing blood sugar control.
Q: Can GEMER 1 Tablet cause weight gain?
A: GEMER 1 Tablet is less likely to cause significant weight gain compared to other diabetes medications. However, some people may experience slight weight gain due to improved blood sugar control and reduced insulin resistance. It is important to monitor your weight and discuss any concerns with your doctor.
Q: What are the customer reviews for GEMER 1 Tablet?
A: Customer reviews of GEMER 1 Tablet are generally positive, with many users reporting improved blood sugar control and fewer side effects compared to other medications.
Q: How should GEMER 1 Tablet be taken?
A: Take GEMER 1 Tablet exactly as prescribed by your doctor. It is usually taken with meals to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects. Swallow the tablet whole with a glass of water. Do not crush or chew the tablet.
Q: Can GEMER 1 Tablet be stopped suddenly?
A: You should not stop taking GEMER 1 Tablet abruptly without consulting your doctor. Discontinuing medication suddenly could lead to unstable blood sugar levels. Always follow your doctor’s guidance when adjusting or discontinuing any medication.
Q: What are the dietary recommendations when taking GEMER 1 Tablet?
A: When taking GEMER 1 Tablet, it is important to follow a healthy, balanced diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins. Avoid excessive sugar and carbohydrate-rich foods. Regular physical activity, along with proper diet, is key to controlling diabetes effectively.
Q: Can GEMER 1 Tablet cause low blood sugar?
A: Yes, Glimepiride, one of the active ingredients in GEMER 1 Tablet, can cause low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), especially if you skip meals, exercise excessively, or take it with certain other medications. It is important to monitor blood sugar levels regularly and follow your doctor’s advice.
Q: What are the common side effects of GEMER 1 Tablet?
A: Common side effects of GEMER 1 Tablet may include nausea or vomiting, diarrhea, stomach upset, low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) and weight gain (due to insulin increase). These side effects usually subside over time as your body adjusts to the medication.
Q: Where can I buy GEMER 1 Tablet online?
A: You can buy GEMER 1 Tablet online at Netmeds. Just visit their website and search for the product, and you will find options to purchase it directly from there.
References
- KD Tripathi MD. Hormones and related drugs. Essentials of medical pharmacology. Seventh edition. New Delhi, May 2013. Page – 274.
- Rakesh Kumar Sahay, Vinod Mittal, G Raja Gopal, Sunil Kota, Ghanshyam Goyal, Mahesh Abhyankar, Santosh Revenkar. Glimepiride and Metformin Combinations in Diabetes Comorbidities and Complications: Real-World Evidence. September 2020. [Accessed on Feb 26th, 2025]

- Sanofi. Efficacy and Safety Comparison of Metformin/Glimepiride Combination Versus Each Compound Alone in New Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Patients (RECOMMEND). NIH U.S. National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov. [Revised in January 2015] [Accessed on Feb 26th, 2025]

- Torrent pharmaceuticals Ltd. Azulix MF. Metformin Hydrochloride Prolonged Release and Glimepiride Tablets I.P. [Revised in July 2019] [Accessed on Feb 26th, 2025]

- Sanofi-aventis group. Amaryl M. Glimepiride + Metformin. [Revised in May 2015] [Accessed on Feb 26th, 2025]