Netmeds First Membership
Quick Links
Introduction About PROLOMET XL 50 TABLET
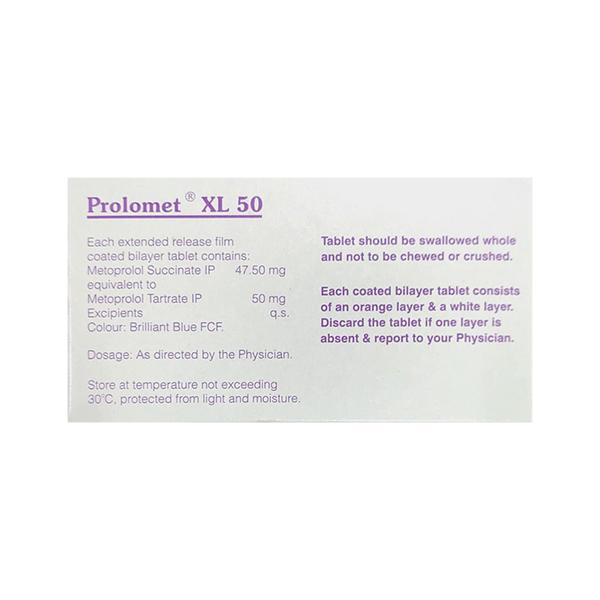
PROLOMET XL 50 Tablet is a medication primarily used to manage conditions such as hypertension, angina, and heart disease. It contains the active ingredient Metoprolol, a beta-blocker that helps to lower blood pressure and improve heart function.
PROLOMET XL 50 Tablet can be prescribed either alone or in combination with other medications. The dosage and frequency will depend on the specific condition being managed and its severity. You can take it on an empty stomach or with food, but it is important to take it consistently at the same time each day to ensure maximum effectiveness. It may take several weeks to experience the full benefits of the medication, and you may need to continue taking it long-term. Even if you feel well, it is crucial to keep taking the medication, as most individuals with high blood pressure do not show symptoms. Stopping the medication could lead to a worsening of your condition.
Common side effect of this medication includes dizziness, fatigue, headache, depression, diarrhea, rash, slow heart rate and nausea. These side effects are typically mild and temporary. In some cases, they may cause shortness of breath or low blood pressure. To minimize the risk of side effects, your doctor will likely begin with a low dose and gradually increase it. If the side effects are bothersome or persist, consult your doctor.
Before taking this medication, inform your doctor if you have any liver problems. It may not be suitable for individuals with a slow heart rate, severe circulation problems, severe heart failure, or low blood pressure. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also consult their doctor before taking it. Be sure to discuss with your doctor whether this medication is appropriate for you. Regular blood pressure checks are recommended to ensure the medication is working effectively. Additionally, avoid alcohol consumption, as it could enhance certain side effects.
Uses Of PROLOMET XL 50 TABLET
- Hypertension
- Angina
- Heart disease
Benefits of PROLOMET XL 50 TABLET
1. Helps reduce high blood pressure (hypertension): Some medicines lower high blood pressure, which can reduce problems like heart disease and strokes. Lowering blood pressure makes the heart’s job easier and helps protect vital organs.
2. Used for managing angina (chest pain): Angina happens when the heart does not get enough oxygen. Medicines can help relax blood vessels, reducing chest pain and making it easier for the heart to get the oxygen it needs.
3. Reduce heart attacks and improves heart function: Certain medications help reduce blood clots, lower cholesterol, and reduce heart strain, all of which can help avoid heart attacks and make the heart work more efficiently.
How PROLOMET XL 50 TABLET Works
PROLOMET XL 50 Tablet contains the active ingredient Metoprolol, which is a beta-blocker medication that works by blocking beta-adrenergic receptors in the heart, reducing the effects of adrenaline. This leads to a decrease in heart rate, blood pressure, and the heart's workload. By reducing the strain on the heart, PROLOMET XL 50 Tablet helps to manage conditions like hypertension (high blood pressure), angina (chest pain), and can also be used to reduce heart attacks and manage heart failure.
How to use PROLOMET XL 50 TABLET
Follow your doctor's instructions regarding the exact dosage. Do not exceed the recommended daily dosage.
How to Take PROLOMET XL 50 Tablet?
- Take one tablet daily with food, to enhance absorption and reduce the risk of stomach upset.
- Swallow the tablet whole with a glass of water. Do not crush or chew the medication.
- For best results, take the tablet at the same time each day.
Recommended dosage of PROLOMET XL 50 Tablet?
- The usual dosage depends on your medical condition, response to management, and other individual factors such as age and kidney function.
- Your doctor may start with a lower dose and adjust it gradually. Always follow your doctor’s instructions for the correct dosage.
What if I forgot to take PROLOMET XL 50 TABLET
- If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as you remember. However, if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose, skip the missed dose, do not double up to make up for the missed one. Always consult your doctor if you are unsure.
Side Effects Of PROLOMET XL 50 TABLET
Like all medicines, PROLOMET XL 50 Tablet may cause certain side effects in some individuals, although not everybody gets them.
The most common side effects of taking PROLOMET XL 50 Tablet are:
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Depression
- Diarrhea
- Rash
- Slow heart rate
- Nausea
When to consult your doctor?
- Severe allergic reaction symptoms such as rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.
- Slow heart rate (bradycardia) symptoms such as dizziness, tiredness, fainting, or feeling weak
- Severe hypotension (Low blood pressure) symptoms such as light-headedness, fainting, blurry vision, or confusion
- Asthma symptoms such as shortness of breath or wheezing
- Angina or heart attack symptoms such as severe chest pain or tightness
- Heart failure or fluid retention symptoms such as swelling of the feet or ankles
- Depression or mood changes symptoms such as unusual tiredness, feelings of sadness, or thoughts of self-harm
- Liver problems symptoms such as yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), dark urine, severe stomach pain, or nausea
- Severe dizziness or fainting
How To Manage Side Effects
Diarrhea
- Drink Fluids: Drink clear fluids such as water, broths, and oral rehydration solutions (ORS).
- Electrolytes: If you are losing a lot of fluids (for example, from frequent diarrhea), consider drinking an electrolyte solution to help replenish lost minerals like potassium and sodium.
- BRAT Diet: Try to take Bananas, Rice (white rice), Apple sauce and Toast (plain, without butter) to control diarrhoea management.
- Avoid Certain Foods: While recovering avoid the following food items such as fatty, greasy, or fried foods, spicy foods, dairy products (especially if you have a temporary lactose intolerance), caffeinated drinks and alcohol and artificial sweeteners like sorbitol.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: You can take over-the-counter anti-diarrheal medications such as loperamide, Bismuth subsalicylate if appropriate for you. Follow the recommended dosage.
Dizziness Or Drowsiness
- Sit or Lie Down: If you feel dizzy, sit down or lie down immediately to prevent falling. Keep your head still and close your eyes if needed.
- Hydrate: Dehydration can cause dizziness, so drink water or electrolyte-replenishing drinks like sports drinks.
- Avoid Sudden Movements: When standing or sitting, do so slowly to avoid triggering dizziness. Take your time when getting up.
- Eat Small, Regular Meals: Low blood sugar can cause dizziness, so eat small meals throughout the day and avoid skipping meals.
- Fresh Air: Sometimes dizziness can be alleviated by taking slow, deep breaths in a well-ventilated area.
Headache
- Rest in a Quiet, Dark Room: Find a calm, quiet space away from bright lights and loud noises. Lie down and close your eyes.
- Hydrate: Dehydration can contribute to headaches, so drink plenty of water.
- Apply a Cold or Warm Compress: A cold pack on your forehead may reduce pain, or a warm compress on your neck or shoulders can relieve tension.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: You can take over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen if appropriate for you. Follow the recommended dosage.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Deep breathing exercises, meditation, or gentle stretching can help reduce stress and alleviate headache symptoms.
Nausea And Vomiting
- Eat Small, Frequent Meals: Avoid heavy or greasy foods. Opt for bland foods like crackers, toast, or bananas.
- Stay Hydrated: Sip on clear fluids like water, ginger tea, or electrolyte drinks, Avoid caffeinated and carbonated beverages.
- Ginger: Ginger is a natural remedy for nausea. Try ginger tea, ginger candies, or ginger ale (ensure it contains real ginger).
- Avoid Strong Odors: Minimize exposure to smells that might trigger nausea, such as perfumes or cooking odors.
Warning & Precautions
Pregnancy
ContraindicatedPROLOMET XL 50 Tablet is not recommended for use in pregnant women. It is important to consult your doctor before taking this medication.
Breastfeeding
ContraindicatedPROLOMET XL 50 Tablet is not recommended for use in breast-feeding women as metoprolol may pass through the breast milk. It is important to consult your doctor before taking this medication.
Driving and Using Machines
Use with CautionDo not drive or operate machines if you experience dizziness or tiredness.
Alcohol
Consult your doctorAvoid consumption of alcohol while taking PROLOMET XL 50 Tablet as it may cause drowsiness and dizziness.
Kidney
Use with CautionPROLOMET XL 50 Tablet should be used with caution in patients with kidney disease such as abnormal function. Dose adjustment of PROLOMET XL 50 Tablet may be needed. Consult your doctor before taking it.
Liver
Use with CautionPROLOMET XL 50 Tablet should be used with caution in patients with liver disease. Dose adjustment of PROLOMET XL 50 Tablet may be needed. Consult your doctor before taking it.
Allergy
ContraindicatedDo not take this medication if you are allergic to metoprolol or any other ingredients in this medicine.
Lungs
ContraindicatedPROLOMET XL 50 Tablet is not recommended for use in patients with bronchospastic diseases like asthma or COPD. Consult your doctor before taking it.
Heart Disease
Consult your doctorPROLOMET XL 50 Tablet is not recommended for use in patients with severe bradycardia, low blood pressure, second or third-degree heart block, cardiogenic shock, decompensated cardiac failure, or sick sinus syndrome (unless a permanent pacemaker is present) and should be used with caution in patients with 1st-degree heart block, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, heart failure, diseases of the heart valve, or enlarged heart muscle. Consult your doctor before taking it.
Use In Pediatrics
Consult your doctorThere is limited data on the use of metoprolol in children and adolescents, so it is generally not recommended unless specifically prescribed by pediatrician. Consult your pediatrician before giving it.
Use In Geriatrics
Use with CautionPROLOMET XL 50 Tablet should be used with caution in elderly patients (aged 65 years and above). Consult your doctor before taking it.
Other Warnings for PROLOMET XL 50 TABLET
Before taking PROLOMET XL 50 Tablet, inform your doctor if you:
- major surgery or anaesthesia
- stroke
- diabetes or low blood sugar
- hyperthyroidism
- peripheral vascular disease
- psoriasis
Who should not take [GBNKEYWORD
PROLOMET XL 50 Tablet is not recommended for use if you:
- severe peripheral arterial disease
- metabolic acidosis
- unmanaged phaeochromocytoma
Safety Advice
- Follow your doctor's instructions regarding the exact dosage.
- Do not exceed the recommended daily dosage.
- Take one tablet daily with food, to enhance absorption and reduce the risk of stomach upset.
- Swallow the tablet whole with a glass of water. Do not crush or chew the medication.
- Avoid with other blood pressure or heart medications (like calcium channel blockers or digoxin) without a doctor's advice.
- Do not take with NSAIDs (like ibuprofen, diclofenac) as they can reduce its effectiveness.
- Avoid alcohol, as it can increase drowsiness and dizziness.
- Let your doctor know if you have kidney problems or liver problems
- Let your doctor know If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant or breastfeeding women.
- Do not suddenly stop taking the medication without consulting your doctor, as this can lead to rebound hypertension or heart issues.
- Regularly monitoring your blood pressure is essential to reduce unexpected decreases.
- Adopting a low-fat diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking may enhance the effectiveness of this medication.
Diet and Lifestyle Advice
What are some heart-healthy foods, tips for reducing sodium intake, and exercises that can improve cardiovascular health?
|
Category |
Heart-Healthy Tips |
|
Heart-Healthy Foods |
- Include fruits and vegetables like berries, leafy greens, and citrus fruits. |
|
Reducing Sodium Intake |
- Limit processed foods like canned soups, salty snacks, and deli meats. |
|
Cardiovascular Exercises |
- Engage in aerobic activities like walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling for at least 150 minutes per week. |
Drug - Drug interaction
Inform your physician if you are taking any of the following medicine before taking PROLOMET XL 50 Tablet:
1. Calcium Channel Blockers (e.g., Diltiazem, Verapamil)
Interaction:
- Both metoprolol (a beta-blocker) and calcium channel blockers can decrease heart rate and blood pressure.
- Taking these medications together can lead to a severe reduction in heart rate (bradycardia), low blood pressure (hypotension), and possibly heart block.
Effect:
- Significant lowering of heart rate, risk of severe hypotension, and potential for heart block.
Management:
- Close monitoring of heart rate and blood pressure.
- Adjusting the dosage of one or both medications, or considering alternative treatments.
2. Antiarrhythmic Drugs (e.g., Amiodarone, Digoxin)
Interaction:
- Metoprolol and antiarrhythmic drugs both lower heart rate.
- Amiodarone may enhance the effects of beta-blockers, increasing the risk of bradycardia and hypotension.
- Digoxin may have an additive effect, further slowing the heart rate.
Effect:
- Increased risk of bradycardia, heart block, and hypotension.
Management:
- Close monitoring of heart rate and ECG, especially during initiation of therapy.
- Adjusting doses as needed or switching to other antiarrhythmic drugs with a lesser impact on heart rate.
3. Antihypertensive Drugs (e.g., ACE inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs), Diuretics)
Interaction:
- Using metoprolol in combination with other antihypertensive drugs may have an additive effect on lowering blood pressure.
- Diuretics can cause electrolyte imbalances, which may exacerbate the side effects of beta-blockers (such as dizziness or fainting).
Effect:
- Hypotension (low blood pressure) may occur.
- Possible electrolyte imbalances that could worsen side effects.
Management:
- Monitor blood pressure and electrolytes regularly.
- Consider dose adjustments for other antihypertensive drugs, particularly diuretics.
4. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Interaction:
- NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen) can reduce the antihypertensive effect of metoprolol by interfering with the kidney’s ability to eliminate sodium and water.
Effect:
- Reduced effectiveness of metoprolol in lowering blood pressure.
Management:
- Use alternative pain management options when possible.
- If NSAIDs are necessary, monitor blood pressure regularly.
5. Insulin and Oral Hypoglycemic Agents
Interaction:
- Beta-blockers like metoprolol can mask the symptoms of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), such as tremors, tachycardia (fast heart rate), and nervousness.
- This can be particularly concerning for diabetic patients on insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents.
Effect:
- Difficulty in recognizing hypoglycemia symptoms, which can lead to severe low blood sugar.
Management:
- Close monitoring of blood glucose levels.
- Educating diabetic patients on how metoprolol may alter hypoglycemia symptoms.
- Consideration of alternative blood pressure-lowering treatments if necessary.
6. Clonidine (Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonist)
Interaction:
- Clonidine can lower blood pressure by acting on the central nervous system, and if stopped suddenly, it can lead to rebound hypertension. When used in combination with metoprolol, the risk of rebound hypertension increases if clonidine is abruptly discontinued.
Effect:
- Risk of significant rebound hypertension and hypertensive crisis.
Management:
- Gradual tapering of clonidine when discontinuing treatment.
- Careful monitoring of blood pressure.
7. Alcohol
Interaction:
- Alcohol can enhance the blood pressure-lowering effect of metoprolol and cause increased drowsiness or dizziness.
Effect:
- Increased risk of hypotension and side effects like dizziness or fainting.
Management:
- Advise patients to limit alcohol intake while on metoprolol.
- Monitor for signs of excessive hypotension and dizziness.
8. CYP2D6 Inhibitors (e.g., Quinidine, Fluoxetine, Paroxetine)
Interaction:
- Metoprolol is metabolized by the CYP2D6 enzyme. Medications that inhibit CYP2D6 (like fluoxetine or quinidine) may increase the plasma concentration of metoprolol, raising the risk of side effects like bradycardia and hypotension.
Effect:
- Increased risk of bradycardia, hypotension, and other beta-blocker-related side effects.
Management:
- Monitor for signs of metoprolol toxicity (e.g., slow heart rate, dizziness).
- Adjust the dose of metoprolol or consider using an alternative drug if necessary.
9. Antiplatelet Drugs (e.g., Aspirin, Clopidogrel)
- Interaction: Combining blood thinners like Warfarin with antiplatelet drugs can increase the risk of bleeding by affecting platelet aggregation and clotting mechanisms.
- Effect: This combination can lead to an increased risk of internal bleeding, bruising, or hemorrhagic stroke.
- Management:
- Avoidance of combining anticoagulants with antiplatelet drugs, unless clinically necessary.
- Close monitoring of signs and symptoms of bleeding.
- Dose adjustment of one or both drugs may be necessary
Synopsis
| Drug | : | Metoprolol |
| Pharmacological Category | : | Beta-blockers |
| Therapeutic Indication | : | High blood pressure, Angina pectoris, Heart failure |
| Dosage Forms | : | Tablet, Capsule, Injection |
More Information
01. How do Metoprolol, Atenolol, and Bisoprolol compare in terms of effectiveness, side effects, and recommended uses?
1. Metoprolol
Effectiveness:
- Indications: Primarily used for hypertension, heart failure, arrhythmias (like atrial fibrillation), and post-myocardial infarction (heart attack) management.
- It’s available in both immediate-release (metoprolol tartrate) and extended-release (metoprolol succinate) forms. The extended-release form is generally preferred for heart failure.
- It can effectively lower blood pressure and heart rate, improve heart function in heart failure, and reduce mortality after a heart attack.
Side Effects:
- Common side effects include fatigue, dizziness, bradycardia (slow heart rate), hypotension, and cold extremities.
- Less commonly, it may cause depression, shortness of breath (especially in people with asthma), and sexual dysfunction.
Recommended Uses:
- Hypertension, chronic heart failure, arrhythmias, and angina.
- Post-heart attack management for reducing the risk of further events.
2. Atenolol
Effectiveness:
- Indications: Used for hypertension, angina, and to prevent further heart attacks. Atenolol has a long half-life, which means it can be dosed once daily.
- It lowers blood pressure and heart rate, but it’s less effective for heart failure compared to other beta-blockers like bisoprolol.
- Atenolol may not be as beneficial in preventing heart failure progression.
Side Effects:
- Similar to metoprolol, common side effects include fatigue, dizziness, bradycardia, and hypotension.
- It may also cause cold extremities and can exacerbate symptoms of peripheral artery disease.
- The long-term use of atenolol has been associated with a slightly higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Recommended Uses:
- Hypertension, angina, and post-heart attack prevention.
- It is not usually preferred for patients with heart failure.
3. Bisoprolol
Effectiveness:
- Indications: Bisoprolol is often considered the most effective beta-blocker for chronic heart failure and hypertension management among the three.
- It is particularly preferred in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and can improve outcomes and reduce mortality in this group.
- Bisoprolol is a once-daily medication with a longer duration of action compared to atenolol and metoprolol.
Side Effects:
- Side effects are similar to other beta-blockers: fatigue, dizziness, bradycardia, hypotension, and cold extremities.
- As with other beta-blockers, bisoprolol may worsen symptoms in patients with asthma or obstructive pulmonary disease.
Recommended Uses:
- Chronic heart failure, hypertension, and arrhythmias.
- Bisoprolol is preferred in heart failure patients because it has more evidence supporting its use and benefits in improving survival.
02.Why Choose PROLOMET XL 50mg over Other Hypertension Medications?
1. Long-Acting Formula for Consistent Blood Pressure Control
- Sustained Release: PROLOMET XL is designed to release Metoprolol gradually throughout the day. This ensures that blood pressure is controlled consistently, providing 24-hour coverage with just one dose.
- Convenience: The once-daily dosing simplifies treatment regimens, improving patient adherence. This is particularly beneficial for patients who may forget to take multiple doses of short-acting medications.
2. Reduced Frequency of Side Effects
- Gentler on the System: Because of its long-acting nature, PROLOMET XL provides smoother blood pressure control without the peaks and troughs seen with short-acting formulations. This reduces the likelihood of side effects like dizziness or sudden blood pressure drops.
- Fewer Side Effects: Metoprolol generally has a favorable side effect profile, and with the XL formulation, patients may experience a lower frequency of side effects like fatigue, bradycardia, or hypotension compared to standard versions of Metoprolol.
3. Improved Patient Compliance
- Easy to Take: With its once-daily dosing schedule, PROLOMET XL may encourage better adherence to prescribed therapy. Consistency is key in managing hypertension, and PROLOMET XL makes it easier for patients to stick to their treatment plan.
- Convenience for Busy Lifestyles: For individuals with hectic schedules or those managing multiple medications, the simplicity of a once-daily pill offers practical convenience, reducing the likelihood of missed doses.
4. Targeted Effect on the Heart and Blood Vessels
- Beta-Blocker Action: As a beta-blocker, Metoprolol works by blocking the effects of adrenaline on the heart, which lowers heart rate and reduces the workload on the heart. This can be particularly beneficial for patients with hypertension and underlying heart conditions such as arrhythmias or previous heart attacks.
- Dual Benefit for Heart and Blood Pressure: PROLOMET XL not only helps in controlling hypertension but also has benefits for patients with coexisting heart conditions like angina or heart failure. It can improve overall cardiovascular health, which is crucial for long-term management.
5. Reduced Risk of Cardiovascular Events
- Cardioprotective Benefits: By lowering blood pressure and reducing heart rate, PROLOMET XL can help reduce the risk of stroke, heart attack, and other cardiovascular complications, which are common in individuals with high blood pressure.
- Better Heart Rate Control: In cases where heart rate management is essential, such as in patients with atrial fibrillation or post-myocardial infarction, PROLOMET XL’s sustained effect can be particularly advantageous in maintaining stable heart rates over time.
6. Fewer Drug Interactions and Side Effects Compared to Other Antihypertensives
- Lower Risk of Electrolyte Imbalances: Unlike certain other antihypertensive medications (such as diuretics), PROLOMET XL does not significantly alter electrolyte levels, which may be a concern for patients taking multiple medications.
- Fewer Risks in Specific Populations: For patients who may experience side effects from other classes of antihypertensives (such as ACE inhibitors, ARBs, or calcium channel blockers), PROLOMET XL may be a better tolerated option.
Conclusion:
PROLOMET XL 50mg (Metoprolol) stands out as a preferred option for hypertension management, especially for patients needing sustained blood pressure control with a reduced risk of side effects. Its once-daily, long-acting formula simplifies adherence and provides consistent cardiovascular protection, making it an excellent choice for long-term management in hypertensive patients, especially those with additional heart-related conditions.
03. What other medications can be used instead of PROLOMET XL for heart and blood pressure management?
|
Medication |
Class |
Active Ingredient |
Primary Use |
Mechanism of Action |
Side Effects |
Common Dosage Forms |
|
PROLOMET XL |
Beta-blocker |
Metoprolol Succinate |
Hypertension, Angina, Heart failure |
Reduces heart rate and blood pressure by blocking beta receptors |
Fatigue, dizziness, slow heart rate, low blood pressure |
Extended-release tablet (50–200 mg) |
|
Atenolol |
Beta-blocker |
Atenolol |
Hypertension, Angina |
Blocks beta receptors, reducing heart rate and blood pressure |
Fatigue, cold extremities, bradycardia, dizziness |
Tablet (25–100 mg) |
|
Lisinopril |
ACE inhibitor |
Lisinopril |
Hypertension, Heart failure, Post-MI |
Inhibits ACE, leading to vasodilation and reduced blood pressure |
Cough, dizziness, hyperkalemia, fatigue |
Tablet (5–40 mg) |
|
Losartan |
ARB (Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker) |
Losartan |
Hypertension, Diabetic nephropathy |
Blocks angiotensin II receptors, reducing blood pressure |
Dizziness, hyperkalemia, headaches |
Tablet (25–100 mg) |
|
Amlodipine |
Calcium Channel Blocker |
Amlodipine |
Hypertension, Angina |
Inhibits calcium ion entry into vascular smooth muscle cells, reducing vascular resistance |
Swelling, dizziness, headache |
Tablet (2.5–10 mg) |
|
Carvedilol |
Beta-blocker & Alpha-blocker |
Carvedilol |
Heart failure, Hypertension, Post-MI |
Blocks beta and alpha-1 receptors, reducing heart rate, blood pressure, and improving heart function |
Dizziness, fatigue, bradycardia, hypotension |
Tablet (3.125–50 mg) |
|
Hydrochlorothiazide |
Diuretic |
Hydrochlorothiazide |
Hypertension, Edema |
Inhibits sodium reabsorption in the kidneys, increasing water loss and reducing blood pressure |
Increased urination, low potassium, dizziness |
Tablet (12.5–50 mg) |
|
Spironolactone |
Aldosterone antagonist |
Spironolactone |
Hypertension, Heart failure, Edema |
Blocks aldosterone, reducing fluid retention and lowering blood pressure |
Hyperkalemia, dizziness, gynecomastia |
Tablet (25–100 mg) |
|
Diltiazem |
Calcium Channel Blocker |
Diltiazem |
Hypertension, Angina, Arrhythmias |
Inhibits calcium channels, reducing heart rate and blood pressure |
Edema, dizziness, bradycardia, fatigue |
Tablet (30–180 mg), Extended-release |
|
Valsartan |
ARB |
Valsartan |
Hypertension, Heart failure |
Blocks angiotensin II receptors, causing vasodilation and reduced blood pressure |
Dizziness, hyperkalemia, headaches |
Tablet (40–320 mg) |
FAQs About PROLOMET XL 50 TABLET
Q: What is PROLOMET XL 50mg Tablet used for?
A: PROLOMET XL is used to manage high blood pressure (hypertension), chest pain (angina), and certain heart conditions.
Q: How does PROLOMET XL 50 work?
A: PROLOMET XL 50 contains the active ingredient metoprolol, which works by blocking the action of certain chemicals in the heart and blood vessels. This helps lower blood pressure, reduces strain on the heart, and prevents irregular heartbeats.
Q: Is PROLOMET XL effective for managing high blood pressure?
A: Yes, PROLOMET XL is effective in lowering high blood pressure by helping to relax blood vessels and reduce the heart's workload.
Q: Can PROLOMET XL 50mg Tablet help with heart palpitations?
A: Yes, PROLOMET XL can help manage heart palpitations by slowing the heart rate and stabilizing irregular heart rhythms.
Q: How long does it take for PROLOMET XL 50mg Tablet to work?
A: It may take a few hours to notice an effect, but the full benefit could take several days of consistent use.
Q: Can I drink alcohol while taking PROLOMET XL 50mg Tablet?
A: It is best to limit alcohol while taking PROLOMET XL, as it may increase side effects like dizziness or drowsiness.
Q: How long can I safely take PROLOMET XL 50mg Tablet?
A: PROLOMET XL can be taken long-term under the guidance of your doctor. Regular check-ups are needed to monitor its effects.
Q: What are the side effects of PROLOMET XL 50?
A: Common side effects of PROLOMET XL 50 include dizziness, fatigue, cold hands and feet, and slow heart rate. Serious side effects, though rare, may include difficulty breathing, swelling of the ankles, and allergic reactions. Always consult your doctor if side effects persist.
Q: Can I take PROLOMET XL with food?
A: Yes, PROLOMET XL can be taken with or without food.
Q: What happens if I miss a dose of PROLOMET XL?
A: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it's almost time for your next dose. Do not double the dose.
Q: Can I take PROLOMET XL 50 with other medications?
A: PROLOMET XL 50 may interact with certain medications, such as other blood pressure medications, blood thinners, heart medications, or diabetes medications. Always inform your doctor about any other medications or supplements you are taking.
Q: Can I stop taking PROLOMET XL 50mg suddenly?
A: No, you should not stop taking PROLOMET XL suddenly. Gradually reduce the dosage as directed by your doctor to avoid complications.
Q: Is PROLOMET XL 50 safe during pregnancy?
A: PROLOMET XL 50 should only be used during pregnancy if clearly needed and prescribed by a doctor. It is important to discuss potential risks and benefits with your doctor.
Q: Can PROLOMET XL 50 cause weight gain?
A: Weight gain is not a common side effect of PROLOMET XL 50, but some people may experience changes in appetite. If you notice significant weight changes, consult your doctor.
Q: Where can I buy PROLOMET XL 50 online?
A: You can buy PROLOMET XL 50 tablet online at Netmeds. Just visit their website and search for the product, and you will find options to purchase it directly from there.
References
1. K D Tripathi. Cardiovascular drugs. Essentials of medical pharmacology. Seventh edition. 2013. Page - 523, 545, 564.
2. Bethesda (MD). Metoprolol. National Institute of Health. NLM. National Centre for Biotechnology Information. PubMed, 2006. [Accessed on 12th March 2025] ![]()
3. Aralez Pharmaceuticals US Inc. Metoprolol. [Revised in December 2016] [Accessed on 12th March 2025] 
4. Dr Reddy’s Laboratories Limited. Metoprolol. [Revised in April 2016] [Accessed on 12th March 2025] 
5. STADA Arzneimittel AG. Metoprolol. [Accessed on 12th March 2025] 
User Feedback