
Netmeds First Membership
Quick Links
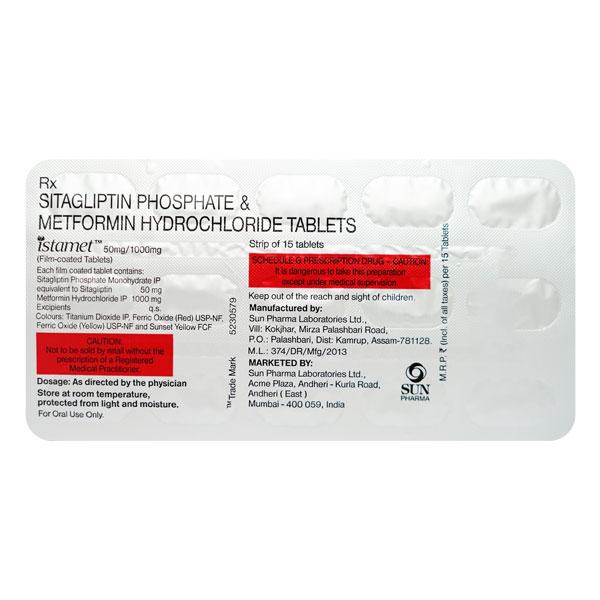
Introduction About ISTAMET 50/1000MG TABLET
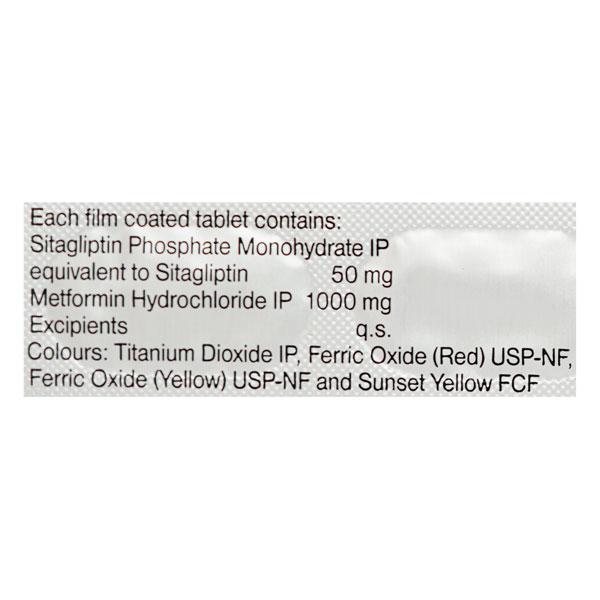
Istamet 50/1000mg tablet is a combination medication used for the effective management of type 2 diabetes. This tablet contains metformin (1000mg) and sitagliptin (50mg), which work together to help control blood sugar levels.
Istamet 50/1000mg Tablet may be prescribed on its own or in combination with other diabetes medications. It is most effective when combined with a healthy diet and regular exercise. The dosage will be determined based on your condition, blood sugar levels, and any other medications you are taking. Taking it with meals can help minimize the risk of stomach discomfort.
To achieve the best results, take the medication consistently at the same time each day, and only stop if advised by your doctor. It is crucial to follow the diet and exercise plan recommended by your doctor while using this medicine. Your lifestyle plays a significant role in managing diabetes.
The most common side effects of this medicine include nausea, dry mouth, metallic taste, dizziness, flatulence, constipation, loss of appetite, headaches, gastrointestinal discomfort, diarrhea, and upper respiratory tract infection. Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can occur as a side effect if you are also using other diabetes medications like insulin or sulfonylureas. It is important to be able to recognize and manage it effectively.
This medication may not be suitable for everyone. Before taking it, inform your doctor if you have a history of kidney, liver, or heart disease, pancreatic problems, or if you consume alcohol heavily. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also consult their doctor before taking this medication. Additionally, certain other medicines may interact with Istamet 50/1000mg Tablet, so it is important to share details of all the medications you are currently taking to ensure your safety. It is advisable to avoid alcohol as it can lower blood glucose levels. Your doctor will monitor your kidney function and blood sugar levels before and during management.
Uses Of ISTAMET 50/1000MG TABLET
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Benefits of ISTAMET 50/1000MG TABLET
- Helps lower blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- The combination of metformin and sitagliptin enhances overall blood sugar control.
- Available in a convenient 15-tablet pack for easy daily use.
How ISTAMET 50/1000MG TABLET Works
Metformin works by decreasing the amount of sugar produced by the liver and improving the body’s sensitivity to insulin, which helps to lower blood sugar levels. Sitagliptin, on the other hand, increases the levels of insulin released by the pancreas in response to meals and decreases the amount of sugar produced by the liver. Together, these medications help to control blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes, improving overall blood glucose control.
How to use ISTAMET 50/1000MG TABLET
Follow your doctor's instructions regarding the exact dosage. Do not exceed the recommended daily dosage.
How to Take Istamet 50/1000mg Tablet?
- Take one tablet daily with meal to reduce the chance of stomach upset.
- Swallow the tablet whole with a glass of water. Do not crush or chew the medication.
- For best results, take the tablet at the same time each day.
What if I forgot to take ISTAMET 50/1000MG TABLET
- If you forget to take your dose, take it as soon as you remember.
- Do not take two doses to make up for a missed dose. This could increase your risk of side effects.
- If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and take your regular dose at the usual time.
Side Effects Of ISTAMET 50/1000MG TABLET
Like all medicines, Istamet 50/1000mg tablet may cause certain side effects in some individuals, although not everybody gets them.
The most common side effects of taking Istamet 50/1000mg tablet are:
- Nausea
- Dry mouth
- Metallic taste
- Dizziness
- Flatulence
- Constipation
- Loss of appetite
- Headaches
- Gastrointestinal discomfort
- Diarrhea
- Upper respiratory tract infection
When to consult your doctor?
- Lactic Acidosis symptoms such as unusual tiredness or weakness, muscle pain, difficulty breathing, unusual sleepiness, stomach discomfort, slow or irregular heartbeat
- Severe Allergic Reaction symptoms such as rash, itching, swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing
- Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia) symptoms such as sweating, shaking, fast heartbeat, hunger, dizziness, confusion, irritability, weakness, or fainting
- Kidney Problems symptoms such as swelling in your hands, ankles, or feet, changes in urine output, or dark-colored urine
- Pancreatitis symptoms such as severe stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, or loss of appetite
How To Manage Side Effects
Diarrhea
- Drink Fluids: Drink clear fluids such as water, broths, and oral rehydration solutions (ORS).
- Electrolytes: If you are losing a lot of fluids (for example, from frequent diarrhea), consider drinking an electrolyte solution to help replenish lost minerals like potassium and sodium.
- BRAT Diet: Try to take Bananas, Rice (white rice), Apple sauce and Toast (plain, without butter) to control diarrhoea management.
- Avoid Certain Foods: While recovering avoid the following food items such as fatty, greasy, or fried foods, spicy foods, dairy products (especially if you have a temporary lactose intolerance), caffeinated drinks and alcohol and artificial sweeteners like sorbitol.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: You can take over-the-counter anti-diarrheal medications such as loperamide, Bismuth subsalicylate if appropriate for you. Follow the recommended dosage.
Dizziness Or Drowsiness
- Sit or Lie Down: If you feel dizzy, sit down or lie down immediately to prevent falling. Keep your head still and close your eyes if needed.
- Hydrate: Dehydration can cause dizziness, so drink water or electrolyte-replenishing drinks like sports drinks.
- Avoid Sudden Movements: When standing or sitting, do so slowly to avoid triggering dizziness. Take your time when getting up.
- Eat Small, Regular Meals: Low blood sugar can cause dizziness, so eat small meals throughout the day and avoid skipping meals.
- Fresh Air: Sometimes dizziness can be alleviated by taking slow, deep breaths in a well-ventilated area.
Nausea And Vomiting
- Eat Small, Frequent Meals: Avoid heavy or greasy foods. Opt for bland foods like crackers, toast, or bananas.
- Stay Hydrated: Sip on clear fluids like water, ginger tea, or electrolyte drinks, Avoid caffeinated and carbonated beverages.
- Ginger: Ginger is a natural remedy for nausea. Try ginger tea, ginger candies, or ginger ale (ensure it contains real ginger).
- Avoid Strong Odors: Minimize exposure to smells that might trigger nausea, such as perfumes or cooking odors.
Warning & Precautions
Pregnancy
ContraindicatedIstamet 50/1000mg tablet is not recommended for use by pregnant women. Therefore, inform your doctor before taking this medicine if you are pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby.
Breastfeeding
ContraindicatedIstamet 50/1000mg tablet is not recommended for use during breastfeeding. Data suggests that the drug may cause toxicity to the baby. It is important to consult your doctor before taking this medication.
Driving and Using Machines
Use with CautionDo not drive or operate machines if you experience dizziness after taking it.
Alcohol
Consult your doctorAlcohol can raise the risk of lactic acidosis and hypoglycemia, so it is recommended to avoid alcohol consumption while taking Istamet 50/1000mg tablet.
Kidney
ContraindicatedIstamet 50/1000mg tablet is not recommended for use in patients with severe kidney disease. Please consult your doctor before taking it.
Liver
Consult your doctorIstamet 50/1000mg tablet is not recommended for use in patients with severe liver problems and should be used with caution in patients with gallstones. Please consult your doctor before taking it.
Allergy
ContraindicatedDo not take this medication if you are allergic to Metformin or Sitagliptin or any other ingredients of this medicine.
Heart Disease
ContraindicatedIstamet 50/1000mg tablet is not recommended for use in patients with severe heart problems (such as acute heart failure or a recent heart attack). Please consult your doctor before taking it.
Use In Pediatrics
ContraindicatedIstamet 50/1000mg tablet is not recommended for use in children and adolescents (under 18 years of age). Consult your pediatrician before giving it.
Use In Geriatrics
Use with CautionIstamet 50/1000mg tablet should be used with caution in elderly patients (aged above 65 years). Please consult your doctor before taking it.
Other Warnings for ISTAMET 50/1000MG TABLET
Before taking Istamet 50/1000mg tablet inform your doctor if you:
- have or ever had pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
- have alcohol dependence
- have high blood lipid levels
- have type I diabetes mellitus (insulin-dependent diabetes)
- are about to have a major surgery
- are fasting
- are malnourished, starved, on an irregular diet, or feeling weak
- perform extreme muscle exercises
- have a vitamin B12 deficiency
Who should not take [GBNKEYWORD
Istamet 50/1000mg tablet is not recommended for use, if you have:
- have severe, uncontrollable diabetes
- have nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or rapid weight loss
- have lactic acidosis or ketoacidosis (a buildup of lactic acid or ketones in the body)
- are dehydrated
- have any severe systemic infection
- have shock or problems in blood circulation
- have problems in breathing
- are an alcoholic
- are scheduled for any X-rays in the upcoming days
Safety Advice
- Follow your doctor's instructions regarding the exact dosage.
- Do not exceed the recommended daily dosage.
- Take one tablet daily with meal to reduce the chance of stomach upset.
- Swallow the tablet whole with a glass of water. Do not crush or chew the medication.
- For best results, take the tablet at the same time each day.
- Follow the prescribed diet and exercise plan along with taking this medication for best results.
- Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly while taking this medicine.
- Alcohol can raise the risk of lactic acidosis and hypoglycemia, so it is recommended to limit or avoid alcohol consumption while taking Istamet 50/1000mg Tablet.
- Let your doctor know if you have kidney problems or liver problems.
- Let your doctor know If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant or breastfeeding women.
- Do not suddenly stop taking the medication without consulting your doctor, as this can lead to uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
- Make sure to keep regular follow-up appointments with your doctor to track your progress and adjust your medication as needed.
Diet and Lifestyle Advice
|
Lifestyle/Diet Factor |
Recommendation |
Benefits |
|
Balanced Diet |
- Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats. |
- Helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and supports overall health. |
|
Carbohydrate Control |
- Choose complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index (e.g., oats, brown rice, quinoa). |
- Helps prevent blood sugar spikes and promotes better glucose control. |
|
Portion Control |
- Use smaller plates, measure portions, and avoid overeating. |
- Prevents overeating, which can lead to weight gain and poor blood sugar control. |
|
Regular Meals |
- Eat 3 balanced meals per day with healthy snacks in between if needed. |
- Helps maintain consistent blood sugar levels throughout the day. |
|
Limit Sugary Foods |
- Avoid sugary snacks, sugary drinks, and processed foods high in added sugars. |
- Reduces the risk of blood sugar spikes and improves insulin sensitivity. |
|
Healthy Fats |
- Include sources of omega-3 fatty acids such as fish, nuts, and seeds. |
- Supports heart health and helps with blood sugar management. |
|
Exercise |
- Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate aerobic activity (e.g., walking, swimming, cycling) most days. |
- Improves insulin sensitivity, helps control weight, and lowers blood sugar levels. |
|
Strength Training |
- Include strength training exercises (e.g., weightlifting, resistance bands) 2–3 times per week. |
- Builds muscle mass, which helps improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. |
|
Weight Management |
- Strive for gradual weight loss if overweight, aiming for 5-10% of body weight reduction. |
- Losing excess weight improves insulin resistance and enhances the effectiveness of medication. |
|
Stay Hydrated |
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Avoid sugary beverages. |
- Proper hydration supports kidney function, helps control hunger, and prevents dehydration. |
|
Limit Alcohol |
- If consuming alcohol, limit to moderate amounts (1 drink/day for women, 2 for men) and avoid sugary mixers. |
- Alcohol in moderation can prevent blood sugar swings and liver complications. |
|
Adequate Sleep |
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. |
- Poor sleep affects insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. |
|
Stress Management |
- Practice relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. |
- Reduces cortisol levels, which helps lower blood sugar and improves overall well-being. |
|
Regular Monitoring |
- Regularly check blood sugar levels as advised by a healthcare provider. |
- Helps track the effectiveness of Istamet and any necessary lifestyle adjustments. |
Drug - Drug interaction
Inform your physician if you are taking any of the following medicine before taking Istamet 50/1000mg tablet:
1. Other Antidiabetic Medications
- Interaction: When Istamet is combined with other oral antidiabetic agents such as sulfonylureas (e.g., glibenclamide), insulin, or other DPP-4 inhibitors (e.g., saxagliptin), there is an increased risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
- Effects: Hypoglycemia can lead to symptoms like dizziness, confusion, sweating, and fainting.
- Management: Close monitoring of blood sugar levels is necessary. Adjusting doses of antidiabetic medications or using non-hypoglycemic agents may help manage this risk.
2. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors
- Interaction: Medications like enalapril, lisinopril, or ramipril, used for blood pressure control, can increase the risk of kidney problems when combined with Metformin, especially if dehydration or renal impairment is present.
- Effects: ACE inhibitors and metformin may together stress the kidneys, leading to acute renal failure, lactic acidosis (a rare but serious side effect of Metformin), or hyperkalemia (high potassium levels).
- Management: Monitoring kidney function (creatinine levels and GFR) is essential. Dose adjustments for Metformin or ACE inhibitors might be necessary. Adequate hydration is also critical.
3. Diuretics (Water Pills)
- Interaction: Diuretics like furosemide or hydrochlorothiazide can affect electrolyte balance and kidney function, which may increase the risk of lactic acidosis in patients taking Metformin.
- Effects: Dehydration or electrolyte imbalances can cause serious complications when combined with Metformin.
- Management: Hydration and regular kidney function monitoring are essential. Patients may need alternative blood sugar-lowering agents.
4. Corticosteroids
- Interaction: Corticosteroids such as prednisone may increase blood glucose levels, reducing the effectiveness of Istamet in controlling blood sugar.
- Effects: Increased glucose production from the liver, leading to hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), potentially worsening diabetes control.
- Management: Close monitoring of blood glucose is necessary, and a dosage adjustment of Istamet or additional insulin may be required during corticosteroid therapy.
5. Alcohol
- Interaction: Drinking alcohol while on Metformin increases the risk of lactic acidosis, especially in high amounts or when combined with other risk factors such as liver or kidney disease.
- Effects: Alcohol can cause hypoglycemia, particularly when taken on an empty stomach, and can exacerbate lactic acidosis.
- Management: Limit alcohol consumption. Patients should avoid drinking large amounts of alcohol, especially without food, and ensure adequate hydration.
6. NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs)
- Interaction: Medications like ibuprofen, naproxen, or celecoxib can increase the risk of kidney impairment, particularly when taken alongside Metformin.
- Effects: Both Metformin and NSAIDs can strain kidney function, leading to a higher risk of kidney injury or lactic acidosis.
- Management: Monitor kidney function regularly. Consider alternative pain relief options that may have a lesser impact on kidney health.
7. Cyclosporine
- Interaction: Cyclosporine (often used in organ transplant patients) can increase the blood levels of Sitagliptin, possibly increasing the risk of side effects like pancreatitis.
- Effects: Elevated levels of Sitagliptin can lead to excessive blood sugar lowering or pancreatic issues.
- Management: Regular monitoring of blood sugar and pancreatic enzymes. Dosage adjustments for Sitagliptin may be required in such cases.
8. Beta-blockers
- Interaction: Medications like atenolol or metoprolol may mask the symptoms of hypoglycemia (such as tachycardia) in diabetic patients on Istamet.
- Effects: Beta-blockers can interfere with the body's ability to respond to low blood sugar, making it harder for patients to recognize and treat hypoglycemia.
- Management: Careful monitoring of blood glucose levels is critical, and patients should be educated on recognizing hypoglycemia without relying on symptoms like increased heart rate.
9. Thyroid Medications (e.g., Levothyroxine)
- Interaction: Thyroid hormone medications can affect metabolism and blood sugar control. If thyroid function is not well managed, it can lead to fluctuating blood glucose levels.
- Effects: Patients may experience unstable blood sugar levels, either hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia, depending on thyroid hormone fluctuations.
- Management: Close monitoring of thyroid function and blood glucose is necessary. Adjustments to the thyroid medication or Istamet dosage may be needed to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Synopsis
| Drug | : | Metformin, Sitagliptin |
| Pharmacological Category | : | Biguanides, DPP-4 Inhibitors |
| Therapeutic Indication | : | Type II diabetes mellitus |
| Dosage Forms | : | Tablet, Capsule, Combi pack |
More Information
01.Product Comparison
a) Istamet Vs Janumet
|
Feature |
Istamet |
Janumet |
|
Active Ingredients |
Metformin + Sitagliptin |
Metformin + Sitagliptin |
|
Brand Name |
Istamet |
Janumet |
|
Drug Class |
Biguanide (Metformin) + DPP-4 Inhibitor (Sitagliptin) |
Biguanide (Metformin) + DPP-4 Inhibitor (Sitagliptin) |
|
Primary Use |
Type 2 Diabetes management |
Type 2 Diabetes management |
|
Mechanism of Action |
- Metformin: Reduces glucose production in the liver. |
- Metformin: Reduces glucose production in the liver. |
|
Dosage Forms |
Tablets, usually 500 mg/850 mg/1000 mg |
Tablets, usually 50 mg/100 mg/500 mg |
|
Common Side Effects |
- Gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhea, nausea) |
- Gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhea, nausea) |
|
Contraindications |
- Severe kidney impairment |
- Severe kidney impairment |
|
Drug Interactions |
May interact with other diabetes medications, diuretics, and blood pressure meds |
May interact with other diabetes medications, diuretics, and blood pressure meds |
|
Weight Impact |
Typically weight-neutral or slight weight loss |
Typically weight-neutral or slight weight loss |
|
Administration |
Taken orally, usually once or twice daily with food |
Taken orally, usually once or twice daily with food |
|
Additional Notes |
Often considered a first-line treatment for Type 2 diabetes |
May have a slightly more favorable dosing flexibility (various dose combinations available) |
b) Istamet Vs Glucophage
|
Feature |
Istamet |
Glucophage |
|
Active Ingredients |
Metformin + Sitagliptin |
Metformin |
|
Drug Class |
Biguanide + DPP-4 inhibitor |
Biguanide |
|
Mechanism of Action |
Metformin reduces glucose production in the liver and increases insulin sensitivity. Sitagliptin inhibits DPP-4, leading to increased levels of incretin hormones, which enhance insulin release and reduce glucagon secretion. |
Metformin reduces glucose production in the liver and improves insulin sensitivity in muscles and fat cells. |
|
Indication |
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
|
Dosage Forms |
Oral tablets (fixed-dose combination) |
Oral tablets |
|
Common Side Effects |
Nausea, diarrhea, headache, upper respiratory infections, upper abdominal pain |
Nausea, diarrhea, upset stomach, vitamin B12 deficiency, lactic acidosis (rare but serious) |
|
Weight Impact |
May cause modest weight loss or weight neutrality |
Weight loss or weight neutrality |
|
Risk of Hypoglycemia |
Lower risk of hypoglycemia (unless combined with other medications) |
Lower risk of hypoglycemia (unless combined with other medications) |
|
Kidney Considerations |
Use with caution in patients with renal impairment |
Contraindicated in severe kidney dysfunction (eGFR < 30 mL/min) |
|
Cardiovascular Benefits |
Sitagliptin has shown some evidence of cardiovascular benefits in certain studies |
Metformin has cardiovascular benefits and is often first-line therapy for patients with heart disease or risk factors. |
|
FDA Approval |
Approved for use in Type 2 Diabetes |
Approved for use in Type 2 Diabetes |
|
Combination Therapy |
Can be used as part of a combination therapy with other diabetes medications |
Can be used as part of combination therapy with other diabetes medications (e.g., sulfonylureas, SGLT-2 inhibitors) |
FAQs About ISTAMET 50/1000MG TABLET
Q: What is Istamet 50/1000mg Tablet used for?
A: It is used to manage blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes.
Q: How long does it take for Istamet 50/1000mg to work?
A: You may start seeing effects within a few days to weeks, but full benefits could take longer, depending on your individual response.
Q: Is Istamet 50/1000mg a generic medicine?
A: Yes, Istamet is a generic medication, typically a combination of metformin and sitagliptin.
Q: Can I stop taking Istamet 50/1000mg suddenly?
A: You should not stop taking it suddenly without consulting your doctor, as it could cause your blood sugar to rise.
Q: How long should I take Istamet 50/1000mg?
A: You will need to take it as prescribed by your doctor, usually long-term, to help manage your diabetes.
Q: Is Istamet 50/1000mg available over the counter?
A: No, it is a prescription medication and requires a doctor's prescription.
Q: Can I use Istamet with other diabetes medications?
A: Yes, Istamet can be used with other diabetes medications, but your doctor will guide the combination.
Q: Can I take Istamet if I have kidney or liver issues?
A: If you have kidney or liver problems, consult your doctor before using Istamet, as adjustments may be needed.
Q: How soon will I see results with Istamet?
A: Initial effects might be visible in a few days, but significant improvements could take a few weeks.
Q: Can I take Istamet 50/1000mg for type 1 diabetes?
A: No, Istamet is typically not used for type 1 diabetes. It is designed for type 2 diabetes.
Q: Can Istamet 50/1000mg be used for weight loss?
A: While weight loss is not its primary use, it may help with slight weight reduction as a side effect for some people.
Q: What is the recommended dosage of Istamet 50/1000mg?
A: The typical dosage of Istamet 50/1000mg tablet is one tablet taken orally once daily with meals to reduce the risk of stomach upset. However, the exact dosage should be determined by your doctor based on individual needs.
Q: What are the common side effects of Istamet 50/1000mg tablet?
A: Common side effects of Istamet 50/1000mg tablet may include nausea, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, or low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Contact your doctor if side effects persist or worsen.
Q: Are there any lifestyle changes I should follow while taking Istamet 50/1000mg tablet?
A: Along with taking Istamet 50/1000mg tablet, it is essential to follow a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and monitor your blood sugar levels as recommended by your doctor to effectively manage type 2 diabetes.
Q: Where to buy Istamet 50/1000mg Tablet online?
A: You can buy Istamet 50/1000mg tablet online at Netmeds. Just visit their website and search for the product, and you will find options to purchase it directly from there.
References
1. KD. Tripathi. Insulin, Oral Hypoglycaemic Drugs and Glucagon. Essentials of medical pharmacology. Seventh edition. 2013. Page-274 & 275.
2. Erin L. St. Onge, Shannon Miller and Elizabeth Clements. Sitagliptin/Metformin (Janumet) as Combination Therapy in the Treatment of Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus. NIH. National Library of Medicine. National Center for Biotechnology Information. PMC. PubMed Central. December 2012. [Accessed on 17th March 2025] ![]()
3. Chitrabhanu Ballav and Stephen C.L. Gough. Safety and Efficacy of Sitagliptin-Metformin in Fixed Combination for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Libertas Academica. 2013. [Accessed on 17th March 2025] 
4. Merck Sharp & Dohme (UK) Limited. Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC) [Revised in February 2022] [Accessed on 17th March 2025] 
5. Merck & Co., Inc. JANUMET® (sitagliptin and metformin hydrochloride) tablets, for oral use. [Revised in July 2022] [Accessed on 17th March 2025] 
6. Milpharm Limited. Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). [Revised in June 2020] [Accessed on 17th March 2025] 
7. Rx Farma Limited. Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). [Revised in September 2019] [Accessed on 17th March 2025] 
8. Organon Pharma (UK) Limited. Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). [Revised in November 2021] [Accessed on 17th March 2025] 
User Feedback